
Malassezia is a yeast that is present in all dogs, but only in some it will cause problems. Mainly in those who already suffer some circumstance that alters the natural balance of their skin.
Below we will explain the consequences that a malasezia overpopulation has for the dog, as well as the symptoms and all the data that will help us to successfully treat this dermatological pathology.
- You may also like: Otitis in dogs
Index of contents
- 1 What is Malassezia?
- 2 How does a malasezia infestation originate in dogs?
- 3 Symptoms of Malassezia in Dogs
- 4 Malassezia otitis
- 5 Malassezia pododermatitis
- 6 Which dogs does malasezia affect?
- 7 How is malasezia diagnosed?
- 8 Treatment for Malassezia in Dogs
- 9 Is Malassezia Contagious?
What is Malassezia?
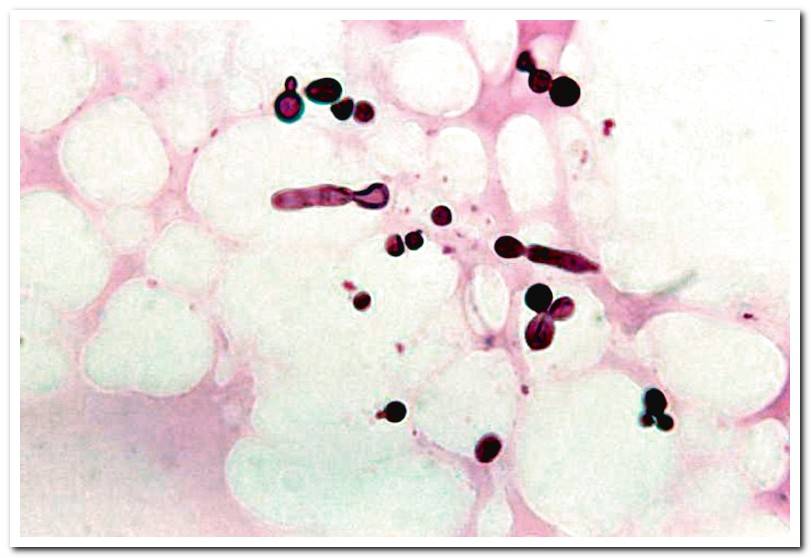
The malassezia that we will find in dogs is, above all, the Malassezia pachydermatis species. It is a yeast, which is a fungus, visible under a microscope and with a peanut-like appearance. It is lipophilic, which means it has an affinity for lipids. A malasezia overpopulation can cause dermatitis in our dogs.
How does a malasezia infestation originate in dogs?
Malassezia is an organism commonly found in the skin and mucosa of dogs and other animals. When some factor upsets the natural balance of healthy skin, the population of Malassezia skyrockets, goes haywire, and becomes pathological.
Allergies and disorders that affect the outermost layer of the skin are the diseases that a dog usually suffers in which We will also see an overgrowth of Malassezia. This is encouraged thanks to a wetter, warmer, more greasy environment and a decrease in defenses. It is more common in hot seasons.
Hormonal diseases that have immunosuppressive effects on the body, as well as prolonged or non-treatment with corticosteroids or antibiotics or disorders that increase the secretion of the sebaceous glands are other factors that are related to an increase in the population of Malassezia.
Symptoms of Malassezia in Dogs
A pathological malasezia infestation is more common in the folds of the dog’s body, where the most favorable conditions for its proliferation exist. The symptoms that are most often associated with an increase in the Malassezia population are as follows:
- Inflammation.
- Variable intensity itching.
- Different skin lesions.
- Alopecia.
- Erythema, which is redness of the skin.
- Flaking, especially fat, although there will be cases of dry.
- Thickening of the skin.
- Hyperpigmentation, that is, the skin appears darkened.
- Scabs.
- Stale smell
- Folliculitis occurs in some cases at the same time.
- Dermatological problems originate in the abdomen and extend to the armpits, groin, and neck.
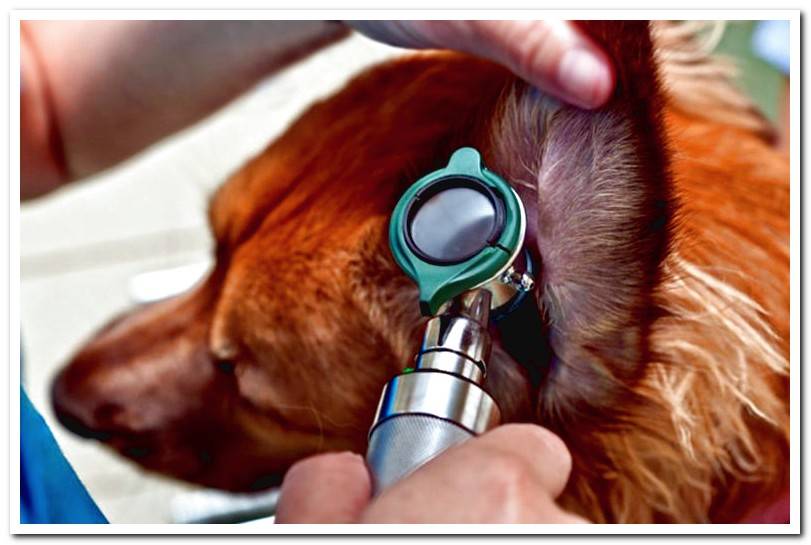
Malassezia otitis
Invasion of this yeast, which is also found naturally in the ear canal, sometimes it is responsible for otitis. This is characterized by a dark brown ceruminous discharge and redness of the pinna. It is easy to be accompanied by a bacterial infection.
Malassezia pododermatitis
When the malasezia overgrowth affects the dog’s feet, it causes a redness between the toes. If the nails are involved, they will have a brown discoloration at their base.
- Symptoms of pododermatitis in dogs
Which dogs does malasezia affect?
Any dog can be affected if, due to any circumstance, an imbalance in its fur occurs. It is more common in adults and in those breeds with a predisposition to suffer dermatological problems such as allergies. For example, it is the case of Westy.
Breeds that are characterized by having skin with abundant folds, such as shar pei, also will be at increased risk of overcrowding in Malassezia. Other breeds that are most frequently affected are the Poodle, the Basset, the Shih Tzu, the Pekingese, the Cocker, the Labrador or the German Shepherd.
How is malasezia diagnosed?
Malassezia will be on the skin of all dogs on a regular basis and without them suffering any pathology. To observe these yeasts, the vet takes a skin sample and visualizes the cells under a microscope. As there is going to be Malassezia, only when their number is excessive may be interpreted as responsible for the dog’s disease.
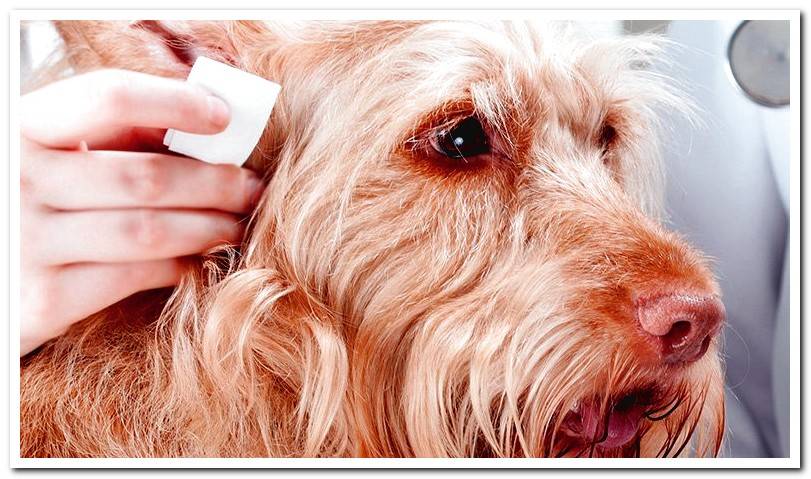

Treatment for Malassezia in Dogs
For the treatment of Malassezia the vet, depending on the picture that the dog manifests, can choose different options. It is possible to prescribe antifungals by mouth, baths with shampoos with a degreasing effect, in addition to being active against fungi, or ointments, especially when the lesions are very localized.
When the malasezia has proliferated in the ears, the vet should examine the ear canal to determine the concurrence of other pathogens such as bacteria. In these cases, this professional will tell us how to clean the ears and will prescribe the most appropriate drug.
Since the malasezia expands thanks to an imbalance in our dog, it is essential to look for what primary cause is weakening the animal. Of course, treatment should also be directed against her.
Is Malassezia Contagious?
All dogs will have malassezia on their skin, so there is no need to worry about a contagion, but to take care of them so that they do not suffer any immune imbalance that may lead to the overgrowth of this yeast. Under normal conditions, Malassezia pachydermatis is not a problem for humans.
